Cooperation: The Individual Perspective (Part 1)
How to get others to cooperate even in a hostile environment towards shared success
Hey there! I’m Robert. Welcome to a free edition of my newsletter. Every week, I share 1 piece of advice 📖, 1 breakthrough recommendation 🚀, and 1 challenge 💥 to help leaders in tech achieve a growth mindset, transform their communication & influence, and master their emotions. Subscribe today to become the person and leader that people love, respect, and follow.
The Christmas Truce of 1914: it’s December—British and German soldiers on both sides of World War I are entrenched in one of the most brutal, bloody conflicts the world has ever seen.
But something strange happens in the middle of this stalemate in the trenches…
The fighting suddenly stops.
The soldiers—on both sides—start to cooperate.
They agree not to shoot at each other, signaling peace through gestures and even smoke from shared fires.
Soldiers stop firing their weapons, rest, and even exchange food across enemy lines.
They created a temporary truce, cooperation in an uncooperative environment.
This unlikely peace was The Christmas Truce of 1914, and it was an incredible, real-life example of how cooperation can emerge in the most unlikely of places—even in the trenches of war.
It is fascinating to think that in literal warfare, cooperation can emerge.
→ It begs the questions—how and why?
→ And how can this knowledge be leveraged in business, leadership, and product development?
Moving fast and shipping great products across big teams requires great cooperation. Especially in any transformative work that comes with a lot of change.
What does lack of cooperation look like?
Perhaps it’s stubborn organizational culture, deeply ingrained silos between departments, or competing internal interests.
However, the higher up you move in Product, the more responsibility you have with less control on the outcome.
You rely on influence.
So for Product Managers and Product Leaders, the challenge becomes:
→ How do you promote cooperation and maximize long-term outcomes?
Over the years of my career, I’ve learned that cooperation doesn’t just happen by accident—it evolves.
And you can evolve it intentionally.
→ In fact, the best PMs do.
They break down silos with grace and foster an environment where everybody wants to participate.
In this first part of a series of newsletters, I share lessons learned from the book The Evolution of Cooperation by Robert Axelrod, Professor of Political Science and Public Policy at the University of Michigan.
For our purposes in product, there are 2 fundamental questions to think about:
Question 1: Let’s say the environment is fixed, how might I promote cooperation and maximize long term outcomes?
Question 2: Let’s say the environment is changeable, how might I architect and shape the environment to promote cooperation and maximize long term outcomes?
The rest of this writing focuses on Question 1.
Check out Part 2 next week, focused on Question 2.
This Week’s ABC…
Advice of the Week: How cooperation drives long-term success and what we can learn from the Tit for Tat strategy.
Breakthrough Recommendation: The powerful lessons on cooperation from The Evolution of Cooperation and how to apply them to your working environment.
Challenge: One practical step to implement cooperative strategies within your team this week.
📖 Advice Of The Week: 4 Principles To Cooperation
“The most successful strategy wasn’t one that always won the battles—it was one that built relationships and kept them going.” —Robert Axelrod, The Evolution of Cooperation
Cooperation is the act of working together toward a common goal—like researching, designing, building, and delivering products people love.
Great cooperation comes from great culture.
→ Cooperative culture: Minimal red tape. Teammates happy to help each other. People are aligned and moving fast.
→ Uncooperative culture: Lots of red tape. Meetings where people nod their heads, but don’t help. People are not aligned, and their individual goals outweigh bigger goals.
Cooperation with others is like rowing a big boat.
Your boat can only move forward towards an exact destination (e.g. # of users, $ revenue, etc.), from people rowing the boat.
Here’s my logic:
You’re rowing a boat: Imagine every micro-decision and contribution (rowing) moved the boat towards the destination (more revenue, more happy users). This is cooperation.
The boat gets to where it needs to go, faster, when all hands row the same way: Then the function of business success, or getting the boat towards the destination, is a function of promoting the environment in which cooperation is maximized.
A leader’s job is to maximize effective cooperation: By getting all hands rowing the same way intentionally, you maximize cooperation and increase your odds of a successful journey. You can do this in many ways, such as increasing psychological safety.
So how do you maximize cooperation in Product?
To answer this, let’s dig a little into game theory.
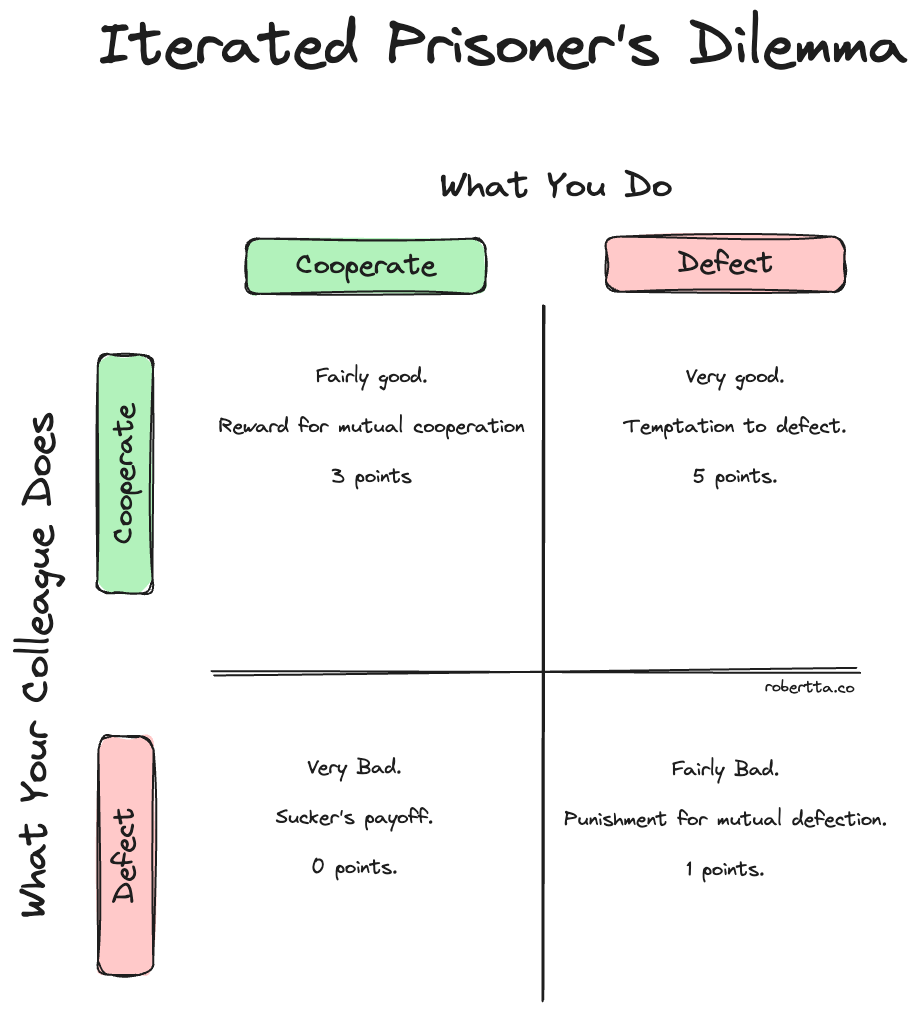
The Iterated Prisoner’s Dilemma
In the late 1970s, Axelrod hosted two tournaments around a basic game from game theory: the Iterated Prisoner’s Dilemma.
It’s a simple game, played for multiple rounds:
→ 2 rational people play
→ Each gets one choice in one round to cooperate or defect
→ They get different points for each outcome
The outcomes:
→ If both cooperate, they receive moderate rewards.
→ If one defects while the other cooperates, the defector gets a large reward, and the cooperator gets nothing.
→ If both defect, they both lose.
Renowned experts from around the world submitted programs for the tournament.
The underlying question: what strategy led to the best long-term outcomes?
→ Interestingly, Axelrod was able to prove that “nice” strategies (cooperative strategies that never defected first) won more often than “mean” strategies (ones that defected early and sought to exploit others for individual gain).
In the first round, the top 8 ranking entries were “nice” strategies.
→ The key insight is that cooperation often emerges as the best strategy over time—particularly when players will have a negligible amount of future interactions with each other.
Against complex, clever strategies, the simplest program was the winner: Tit for Tat.
What is the Tit for Tat Strategy?
The Tit for Tat strategy is simple but powerful:
Start by cooperating.
Reciprocate the opponent’s last move.
If they cooperate, you cooperate.
If they defect, you defect—but only for that round.
If they cooperate again, you cooperate again.
You forgive past transgressions and return to cooperation.
Axelrod breaks down why this simple strategy was so effective, and from that work we are able to reason through what makes effective cooperation.
A Product Management Example:
→ If both cooperate
Example
“Hey can you prioritize this work on your roadmap in the next quarter, to help with our revenue goals?” —a cooperative PM looking for more cooperation
“Yes for sure, I believe we can fit that in the middle of next quarter.”—another cooperative PM, reciprocating cooperation
→ If one defects while the other cooperates
Example
“Hey can you prioritize this work on your roadmap in the next quarter, to help with our revenue goals?” —a cooperative PM looking for more cooperation
*Nods head, does nothing*—an uncooperative PM, focused on their immediate goals (what I call an empty head-nodder)
→ If both defect, they both lose.
Example
Silence—an uncooperative PM, not thinking about cooperation, focused on their own immediate goals
Silence—an uncooperative PM, not thinking about cooperation, focused on their own immediate goals
Notice that in the example for both defect, there’s no communication at all.
I believe that the best PMs overcommunicate by default, because their job is to get all the cross-functional groups rowing the boat the same way.
Lack of communication in PM work, IS uncooperative.
Takeaway: If you’re not communicating in Product work, you’re not cooperating.
How can we learn from Tit for Tat and the research here, as an individual PM?
The Four Key Principles of Cooperation for Individual Participants
Don’t Be Too Envious
→ Tit for Tat doesn’t worry about getting the biggest immediate payoff or comparing its score to others—it’s focused on long-term success.
→ As a product leader, focus on creating and nurturing relationships built on mutual trust and benefit. It’s not a zero-sum game. Everyone can win.Don’t Be the First to Defect (Be Nice)
→ Tit for Tat starts by cooperating. It assumes the best in others and gives them the opportunity to work together.
→ As a product leader, always be cooperative first. Never be the first to “defect”. Don’t be an empty head-nodder.Reciprocate Cooperation and Defection
→ Tit for Tat reciprocates. If the other player cooperates, Tit for Tat cooperates. If they defect, Tit for Tat defects in the next round.
→ As a product leader, this does NOT mean sabotaging others. This means to focus your time and energy on those who are cooperative. If you find yourself engaging with people who are uncooperative, then prioritize your effort and time with others who are cooperative.Don’t Be Too Clever
→ Tit for Tat is simple, clear, and predictable. It doesn’t try to outsmart or manipulate. The strategy’s transparency builds trust because everyone knows how it will respond.
→ As a product leader, this means focus on transparency as a value. People will come to know your brand as cooperative and easy to work with. You will more easily garner buy-in and influence as this compounds over time.
The lesson here is simple: in long-term interactions, cooperation wins.
For the stakeholders whose buy-in and cooperation you depend on for success, increase the surface area of opportunities for collaboration.
Key takeaway: Find ways to make sure your stakeholders know they will need to work with you long term.
So what if you’re the only “nice” player in an environment full of “mean” players?
Can you win?
That brings us to this week’s Breakthrough.
🚀 Breakthrough Recommendation: The Evolution of Cooperation by Robert Axelrod
Can Cooperation Emerge in Hostile Environments?
A strategy is considered collectively stable if no strategy can invade it.
If your working environment is predominantly uncooperative (“mean” strategies), then it means that lack of cooperation is the collectively stable strategy.
So, is it possible for a few cooperative players to “win” (invade) and promote cooperation among larger population of uncooperative (defector) players?
Can a “nice” strategy become the collectively stable one, in a hostile environment?
Remember the World War 1 example?
If it’s possible in the trenches, it’s possible in business.
In fact, Axelrod’s research proves that “nice” strategies can emerge as the collectively stable one even in hostile environments.
→ In other words, yes it is possible for a few cooperative players to “win” in a hostile environment.
Whether you're leading a scrappy startup or managing a complex product team within a big tech company, cooperation is the key to long-term success.
In startups, there is common wisdom that the founding team dynamics are vital to survival. The wrong hire can derail the entire team.
In my (painful) experience, this is true.
In big tech, siloed teams and departmental conflicts often create non-cooperative environments.
In my (painful) experience, this is also true.
The solution is the same for both—foster and protect your team’s cooperation.
How do you do this?
There are two key takeaways from Axelrod’s research to remember:
Takeaway 1: In a predominantly hostile environment (most of the population employs “mean” strategies), it is possible for cooperation to emerge as the collectively stable strategy.
This happens even if the “nice” players cooperate with each other only 5% of the time.
That’s CRAZY to think about.
→ That means that if you’re a PM in a hostile environment, if you even interface with a cooperative individual 5% of the time, cooperation (over a long time period) will emerge as the dominant strategy.
So go find cooperative people, and maximize time with them.
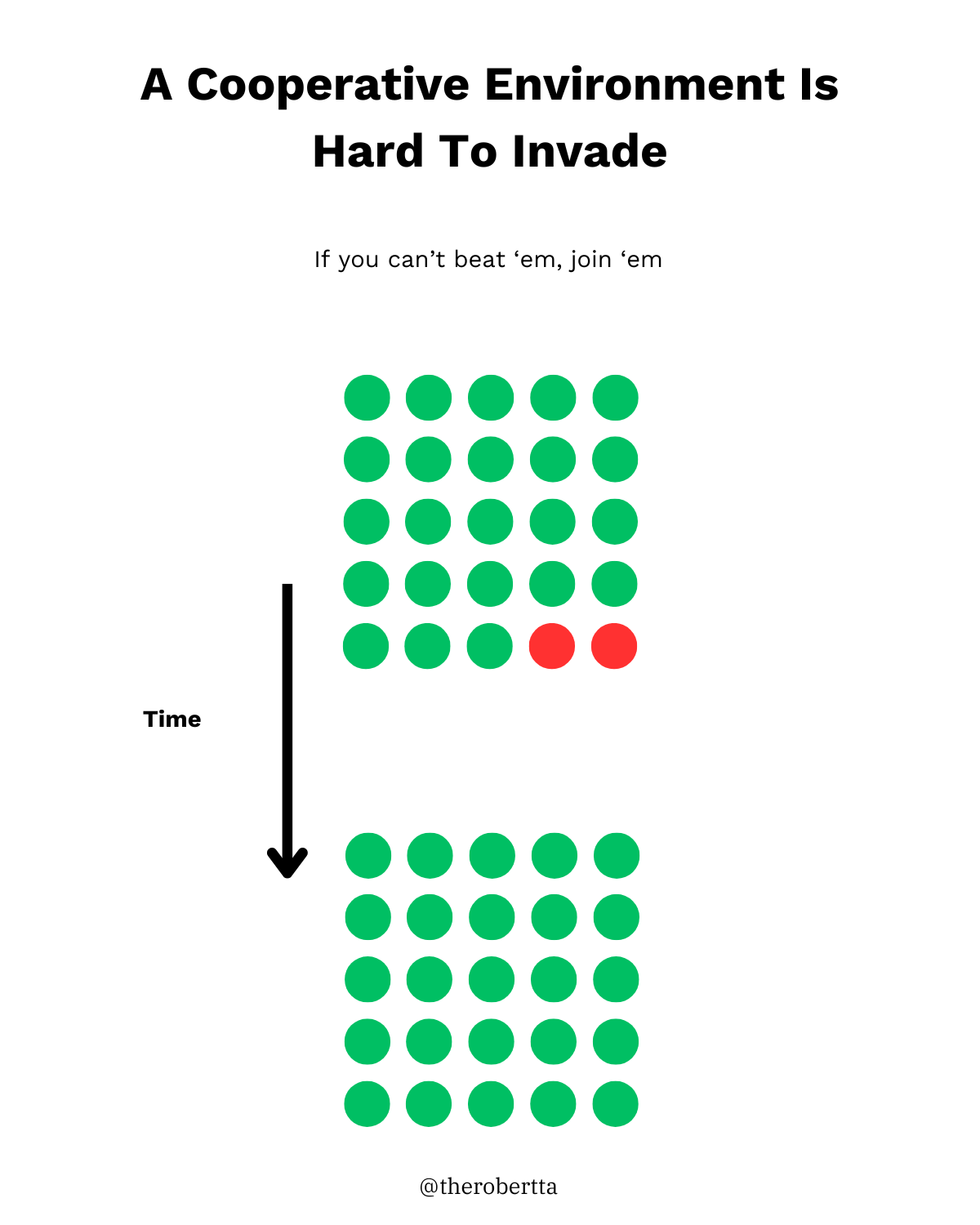
Takeaway 2: In a predominately cooperative environment (most of the population employs “nice” strategies), it is impossible for “mean” strategies to invade.
This is insightful to our work and experiences.
→ That means if you’re a PM in a cooperative environment, you can increase success for everybody by just staying cooperative.
This points to a theme I’ve seen in my career—great (and cooperative) cultures stay great.
This is a obviously an over-generalization.
You can certainly have pockets of “mean” players in a big organization, but Axelrod’s work shows that it would be impossible for their strategy to become the dominant one in a predominantly cooperative organization.
This lines up with the age old saying…
“If you can’t beat em, join em'“.
There is one big takeaway here as an individual in a hostile environment:
Go find allies (fellow cooperative players). Work with them. Focus energy and effort into those relationships. Do this and you will generate more collective success in the long term.
What if there are no allies?
If there are truly ZERO cooperative allies in your company, then I have bad news—you need to start looking for a different job for your health, sanity, and success.
What I Did This Week
I was dealing with a difficult Sr. Director stakeholder whose buy-in and cooperation I need for a big project.
Let’s just say he was employing a “mean” strategy.
Instead of focusing my time and effort on him, I sought out a teammate in his organization and focused my influence efforts there instead.
Now we’re teaming up.
The takeaway: Don’t let uncooperative people stop you from doing great work. Find the cooperative players, and focus your energy and effort on them.
→ If you can’t influence the person, then influence the people around them.
💥 Challenge: Create Opportunities for Cooperation This Week
This week, think about a particularly uncooperative stakeholder.
Be intentional and make friends with teammates in their organization. Nurture that relationship.
You’ll see this pay off in the long term.
You got this!
Next week, we’ll dive into Part 2:
Let’s say the environment is changeable, how might I architect and shape the environment to promote cooperation and maximize long term outcomes?
Stay tuned.
Liked this article? 💚 Click the like button.
Feedback or addition? 💬 Add a comment.
Know someone that would find this helpful? 🔁 Share this post.
P.S. Want reminders on growth, empathy, and leadership? Follow me on LinkedIn, Threads, and Twitter.